
“MAGIC” stands for Major Aspects of Growth in Children
MAGIC AFRICA is a non-profit, patient advocate organization. It is an organization that supports families with children with endocrine growth problems. Magic Africa works together with MAGIC FOUNDATION KENYA (a division of MAGIC Africa) in spreading awareness of endocrine conditions of children all over Africa. Read More
Factors Affecting Child Growth and Development
As a parent, your child’s growth and development is of prime importance to you. There are several factors that affect the growth and development of your child and it is essential to have an understanding of each of the factors, both internal and external. Explore
Babies (0-1yr) 
In the first year, babies learn to focus their vision, reach out, explore, and learn about the things that are around them. Cognitive, or brain development means the learning process of memory, language, thinking, and reasoning. Learning language is more than making sounds (“babble”), or saying “ma-ma” and “da-da”.Expect a growth rate of about 25cm within the 1st year.
Toddlers (2-4yrs) 

During this stage, toddlers should be able to follow two- or three-step directions, sort objects by shape and color, imitate the actions of adults and playmates, and express a wide range of emotions. Two-year-olds are very active and begin to lose the appearance of a baby. Expect a growth rate averaging 10cm per year at this stage.
Children (5-12yrs) 

Understand more about their place in the world and within interpersonal relationships. Pays more attention to friendships and teams. Wants to be liked and accepted by friends. Shows rapid development of mental skills. For 5 to 12-year-olds, there continues to be a wide range of “normal” regarding height, weight and shape. Kids tend to get taller at a steady pace, growing about 2-2.5 inches (6 to 7 centimeters) each year.
Teens (12-17yrs) 

Adolescents will reach their growth spurt around the same time as puberty. Females will experience a growth spurt between ages nine and 15. Males at birth will experience a growth spurt between ages 12 and 17. Each child grows at their own pace and may experience puberty changes earlier or later than their peers. Adolescents will increase in height at an average of 3 to 4 inches (9 to 10 centimeters) during their growth spurt.
Patient Advocacy Services
The patient advocate role is important for patients not only for communication, but also for their mental and emotional health needs as well. Sometimes, all a patient wants and needs from their patient advocate is someone to listen to their fears and concerns.
Find out more about our Patient Advocacy ServicesTackling Children Growth Disorders
Children fail to grow for a variety of reasons such as Hormones, genetics, sleep, nutrition, general health and exercise are all factors for normal growth. If you suspect that your child is not growing normally, you are in the right place! Some of the children growth disorders we tackle include:
Growth Hormone Deficiency

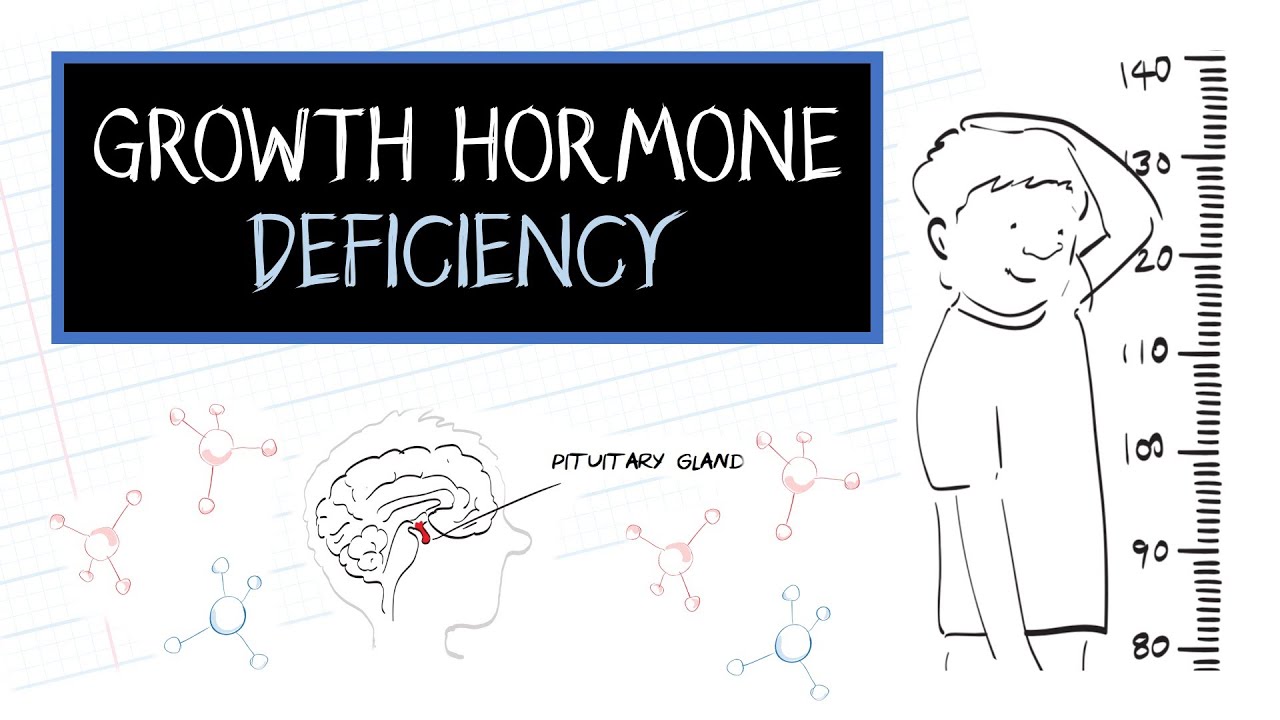
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), also known as dwarfism or pituitary dwarfism, is a condition caused by insufficient amounts of growth hormone in the body.
Achondroplasia / Skeletal Dysplasia

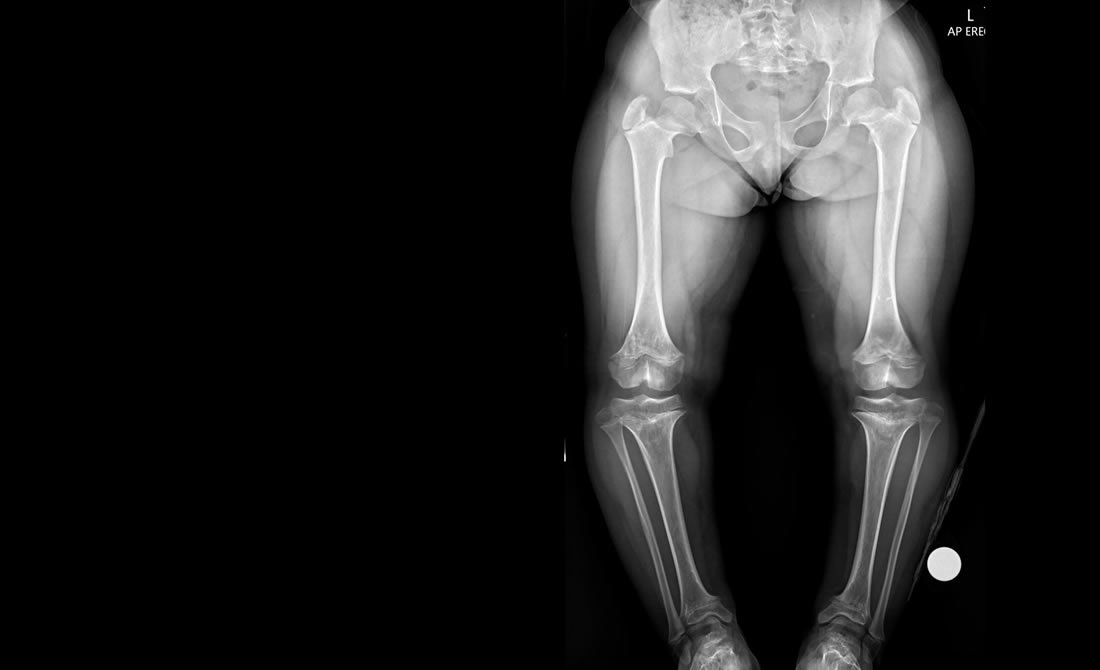
Achondroplasia and other Skeletal Dysplasia is the most common type of short-limbed dwarfism. The condition occurs in 1 in 15,000 to 40,000 newborns.
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)

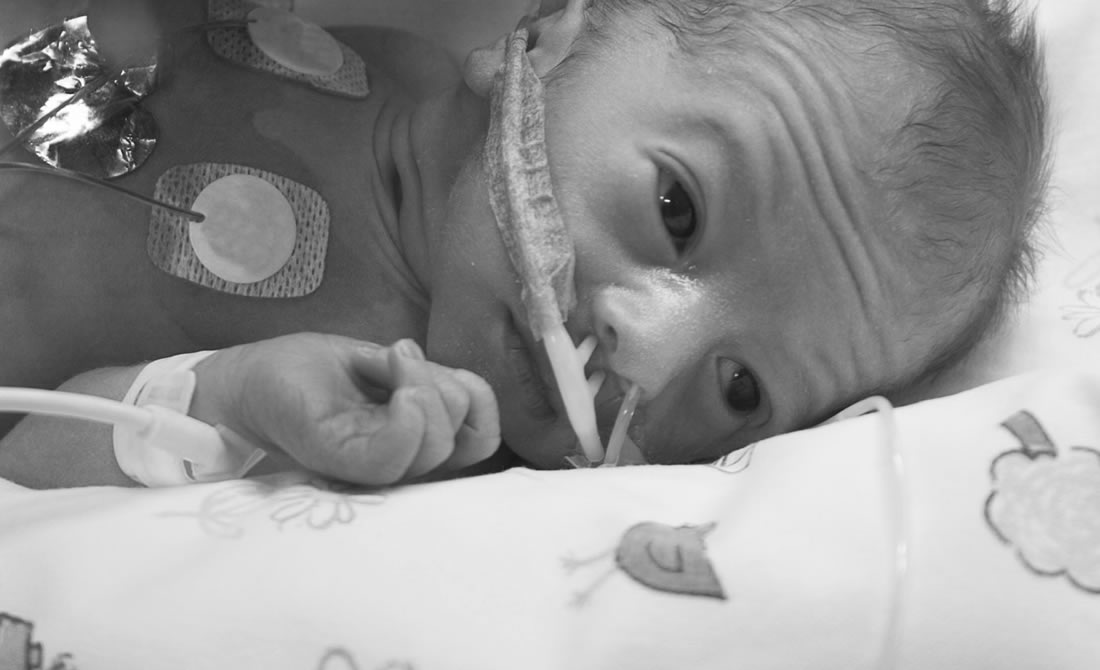
A condition in which a baby doesn't grow to normal weight during pregnancy. Causes vary but include placenta abnormalities, high blood pressure in the mother, infections and smoking or alcohol abuse.
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)

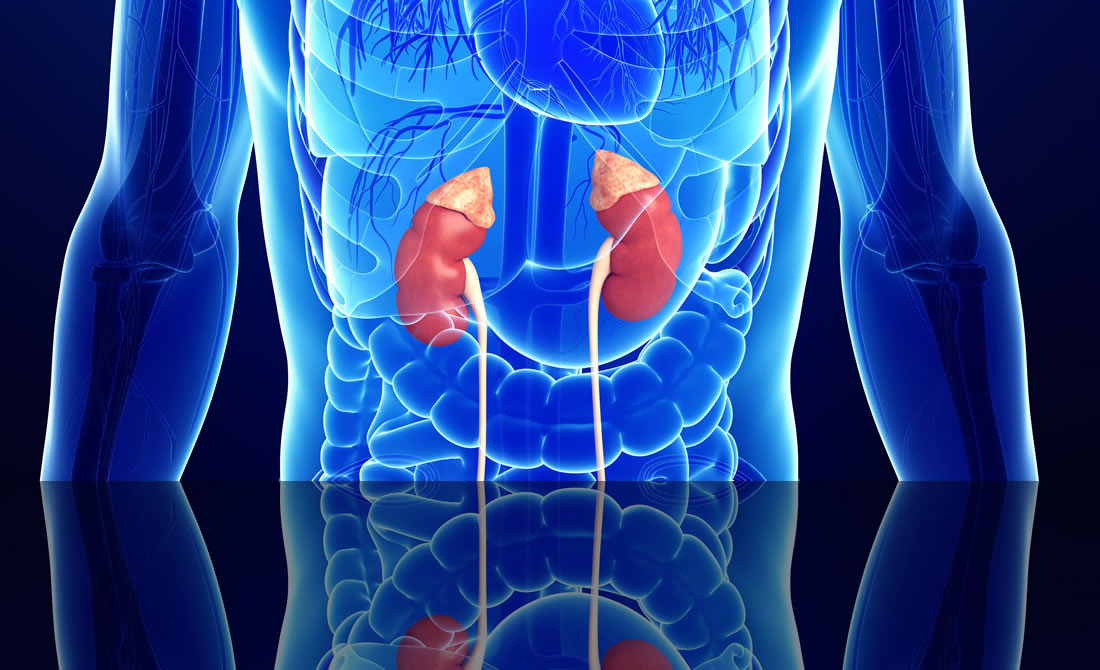
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a genetic disorder in which the two adrenal glands (located at the top of the kidneys) do not function properly.
Small for Gestational Age (SGA)
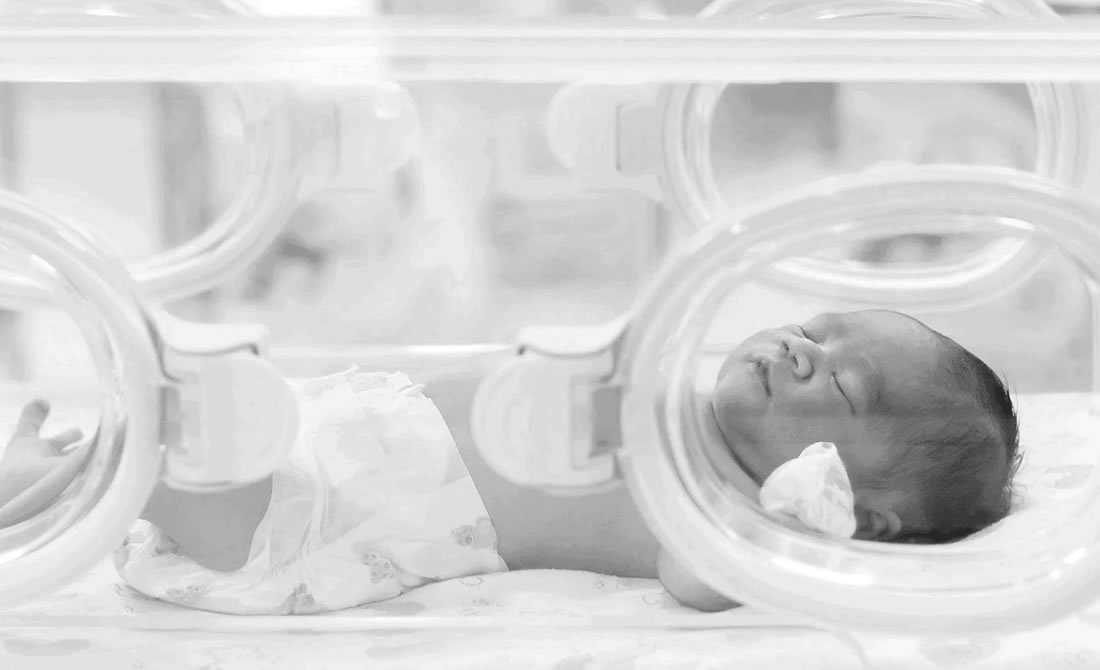


Small for gestational age is a term used to describe babies who are smaller than expected for the number of weeks of pregnancy. These babies have a birth weight below the 10th percentile.
Insulin-like Growth Disorder Factor-1 Deficiency (IGFD)

IGF-1 is a hormone that manages the effects of growth hormone (GH) in your body. Together, IGF-1 and GH promote normal growth of bones and tissues.





